Sukatan Pelajaran Bahasa Inggeris
GRAMMAR
Grammar forms part of the language contents in the syllabus. These items need to be taught in context and in a meaningful way. This can be done through a selection of the items required to teach the listening speaking, reading and writing skills.
The grammar items should not be taught in isolation or as discrete items as far as possible, The range of grammar items to be taught are given in the listing below.
Word Order
Positive and negative statements
Positive and negative questions and responses
Wh questions and responses
What, Where, When, How, Why, Who, Whose, Which
Questions with tags and responses
doesn’t, didn’t, hasn’t, hadn’t, haven’t, wasn’t , weren’t, isn’t aren’t
Requests, imperatives, commands, responses
Sentences types:
Simple, compound
Connectors
Conjunctions
and, but, or, so, while, although, therefore, either……
or, neither….. nor
Sequence connectors
first, next, then, finally, before, after
Verbs
Simple present tense
Simple past tense
Simple future tense
Present continuous tense
Past continuous tense
Future continuous tense
Modals
can, may, might, must, ought to, could,
will, would, shall, should (and with negative forms)
Subject and verb agreement
am, are, is, was, were, has, have, had, do, does, did
Articles
Articles with singular and plural countable nouns, zero articles a, an the
Articles with non-countable nouns
Articles with proper nouns
Prepositions
in, out, on, under, by, beside, near, behind, in front of,
at the back of, over, at, between, among, through, above, around, across, from,
of, off, to
Nouns and Pronouns
Nouns forms - countable, uncountable, collective
Possessives
his, her, hers, theirs, our, mine, its
Pronouns forms
personal - I, he, she, it, they, we, our, us, their
interrogative - who, which, what, whose, where, when, how.
Gender
masculine, feminine, neuter
Modifiers
Adjectives and adverbs
Comparative and superlative forms
skip to main |
skip to sidebar


pusattuisyenkitacemerlang@yahoo.com
We provide 1. Quality Teaching To Encourage Your Child's Learning Desire. 2. Quality Learning To Build Your Child's Self Confidence. 3.Quality Growing To Shape Your Child's Future. Email: pusattuisyenkitacemerlang@yahoo.com
Principal

Motivator and Academic Counselor

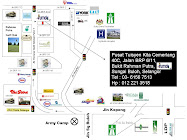
Location

pusattuisyenkitacemerlang@yahoo.com
Sharing Subjects
- Adat Melayu (6)
- B.Melayu - Karangan (1)
- KC 伟 杰 课 室 (25)
- KC 伟 杰 课 室 Proverb (17)
- KC 伟 杰 课 室 Reborn (15)
- KC 伟 杰 课 室- Travel (1)
- KC 伟 杰 课 室-出国留学 (14)
- KC 伟杰课室 - 教育 (10)
- KC 伟杰课室学习 (8)
- Kita Cemerlang (12)
- Kita Cemerlang - Sharing (106)
- Kita Cemerlang 雙溪毛糯- Work? (10)
- Komsas (6)
- Math Reference Tables (10)
- Maths Olympics (8)
- Photos (4)
- PMR - BM作文 (12)
- PMR - 华文 (17)
- PMR - 华文作文 (25)
- PMR - 英语 (1)
- PMR - 英语作文 (6)
- PMR-华语-孔子 (4)
- Science - Chemistry (9)
- SPM - B. M-Tatabahasa (2)
- SPM - BM作文 (20)
- SPM 华文 (4)
- SPM 华文作文 (3)
- STPM 华文 (4)
- STPM 华文作文 (1)
- Teacher (7)
- UPSR - 华语 (2)
- UPSR - 华语作文 (54)
- UPSR - 成语故事 (9)
- UPSR B.English (13)
- UPSR B.English - Grammar (28)
- UPSR B.English - Story (7)
- UPSR B.English Essay (16)
- UPSR B.M- Nilai Murni (5)
- UPSR B.Melayu (3)
- UPSR B.Melayu - Karangan (15)
- UPSR B.Melayu - Tatabahasa (20)
- UPSR Mathematic (11)
- UPSR- 华语 (39)
- UPSR- 华语古文 (21)
- UPSR- 科学 (17)